What is CycBox?
A next-gen IoT debugging toolkit for engineers and developers, featuring high-performance multiprotocol support, Lua scripting automation, and real-time data visualization for efficient debugging of serial devices, network protocols, and embedded systems.
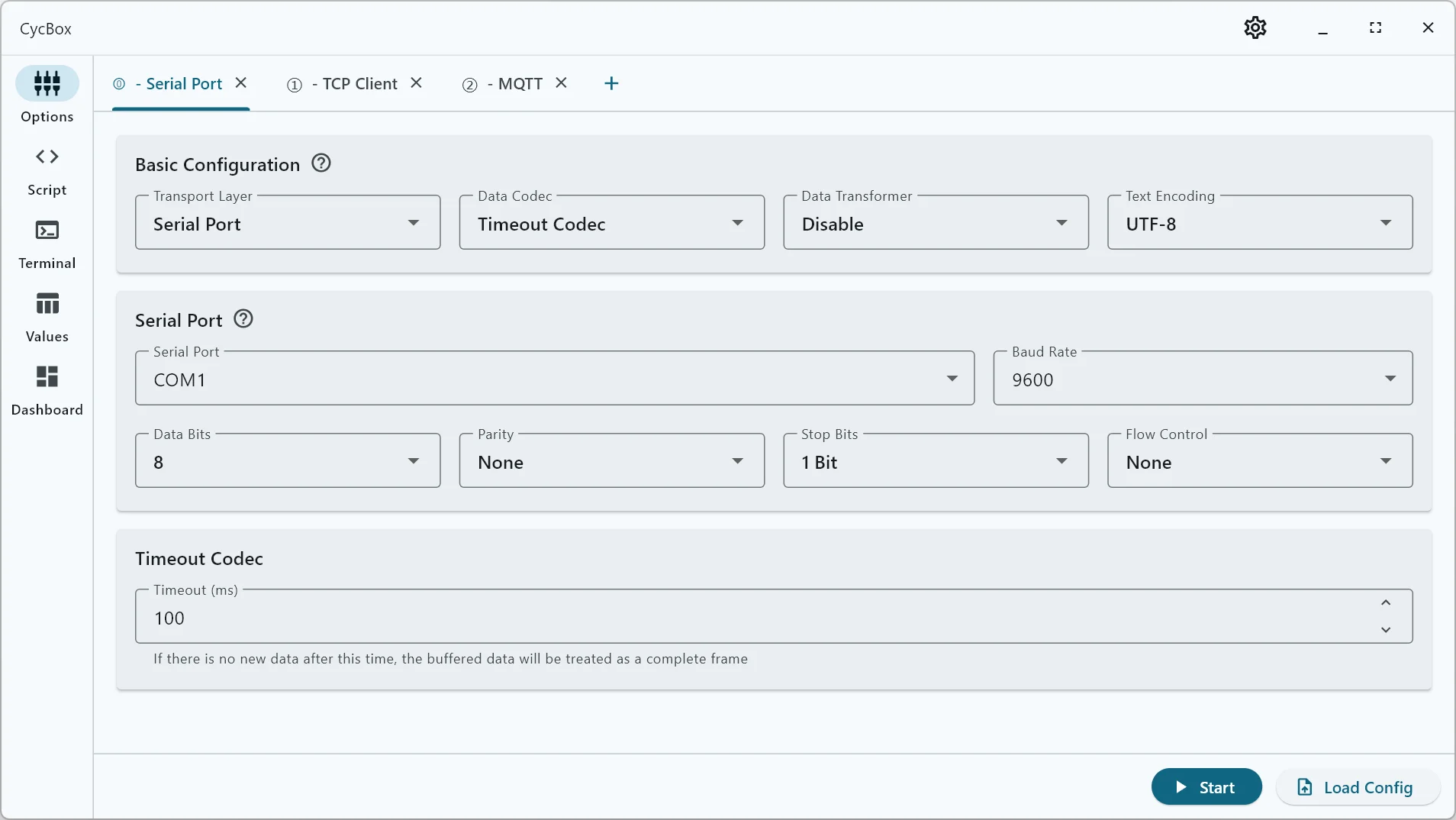
Enhanced Multi-Protocol Support
Offers seamless connectivity across Serial, TCP, UDP, WebSocket, and MQTT protocols, with robust data bridging capabilities. Supports widely-used standard protocols such as AT commands, Modbus RTU, and Modbus TCP, while also providing flexibility for custom frame structure development.
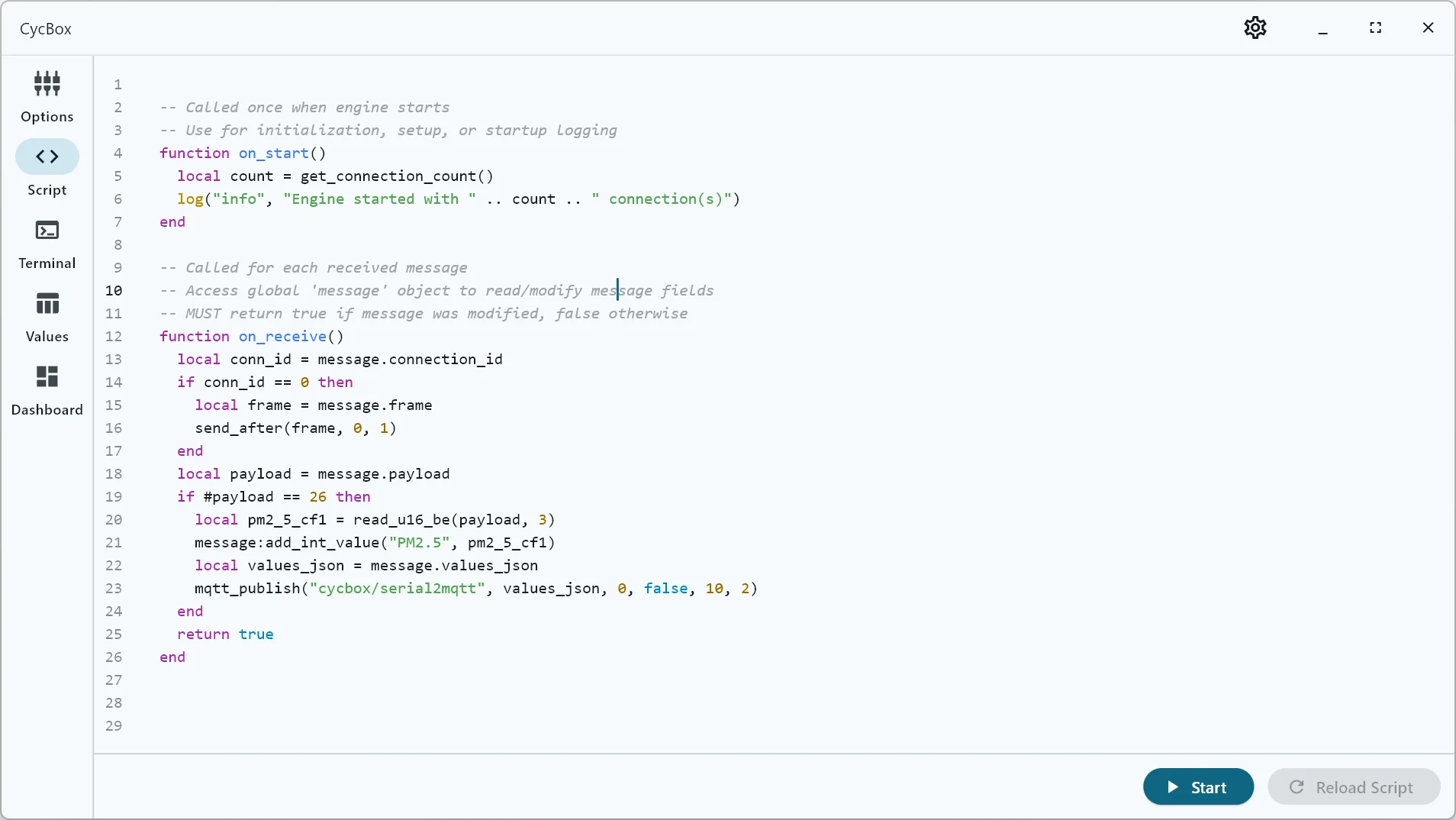
Automation with Lua Scripting
Develop custom automation workflows effortlessly using Lua scripting. Handle incoming data, generate dynamic responses, validate protocol compliance, and execute intricate test sequences—all with no manual intervention.
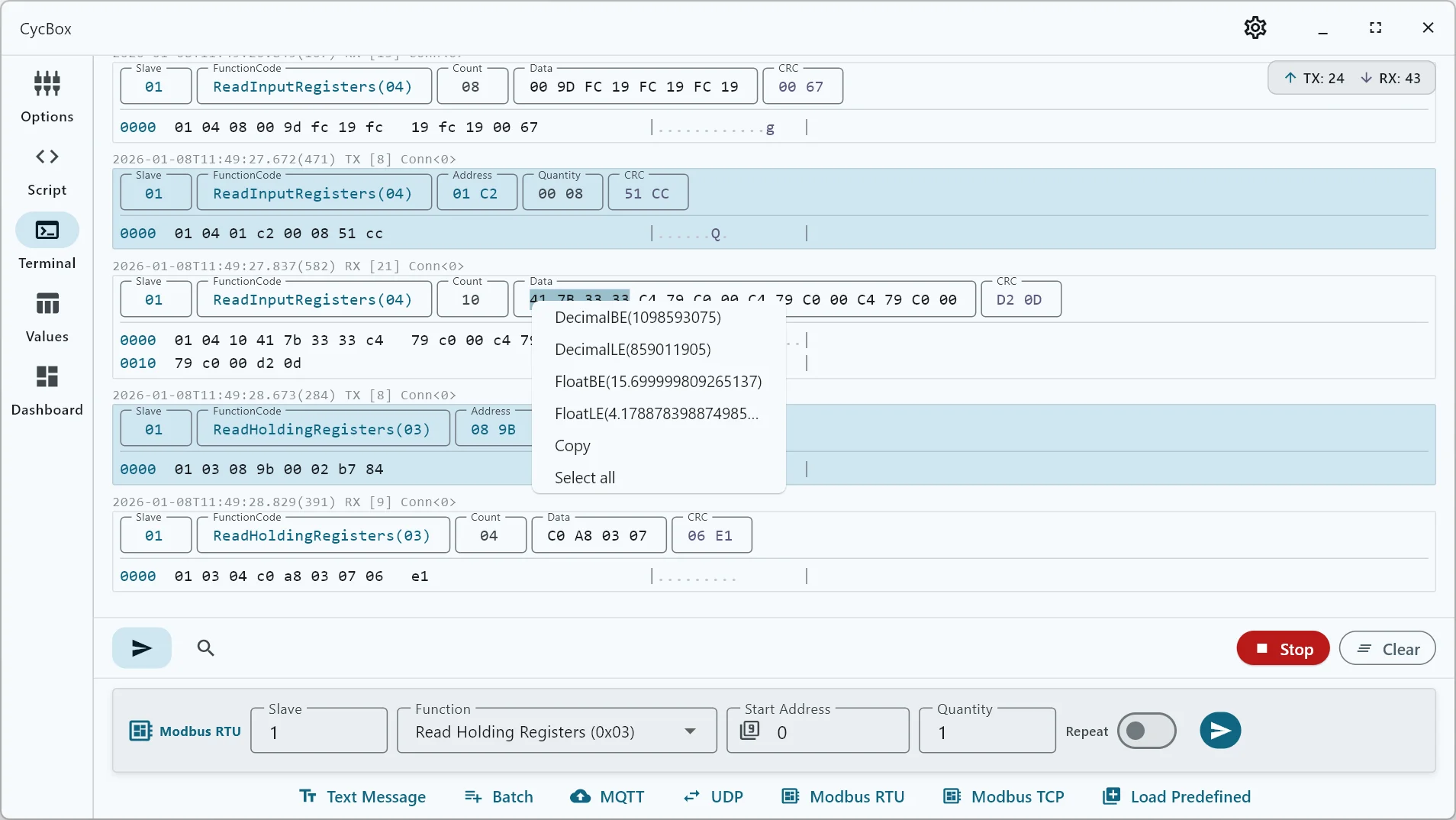
Efficient User Interface
Provides an information-rich message display and a protocol-aware message sending box. Includes advanced features such as scheduled transmissions, configurable message sequences, and a robust search function with keyword highlighting and message filtering.
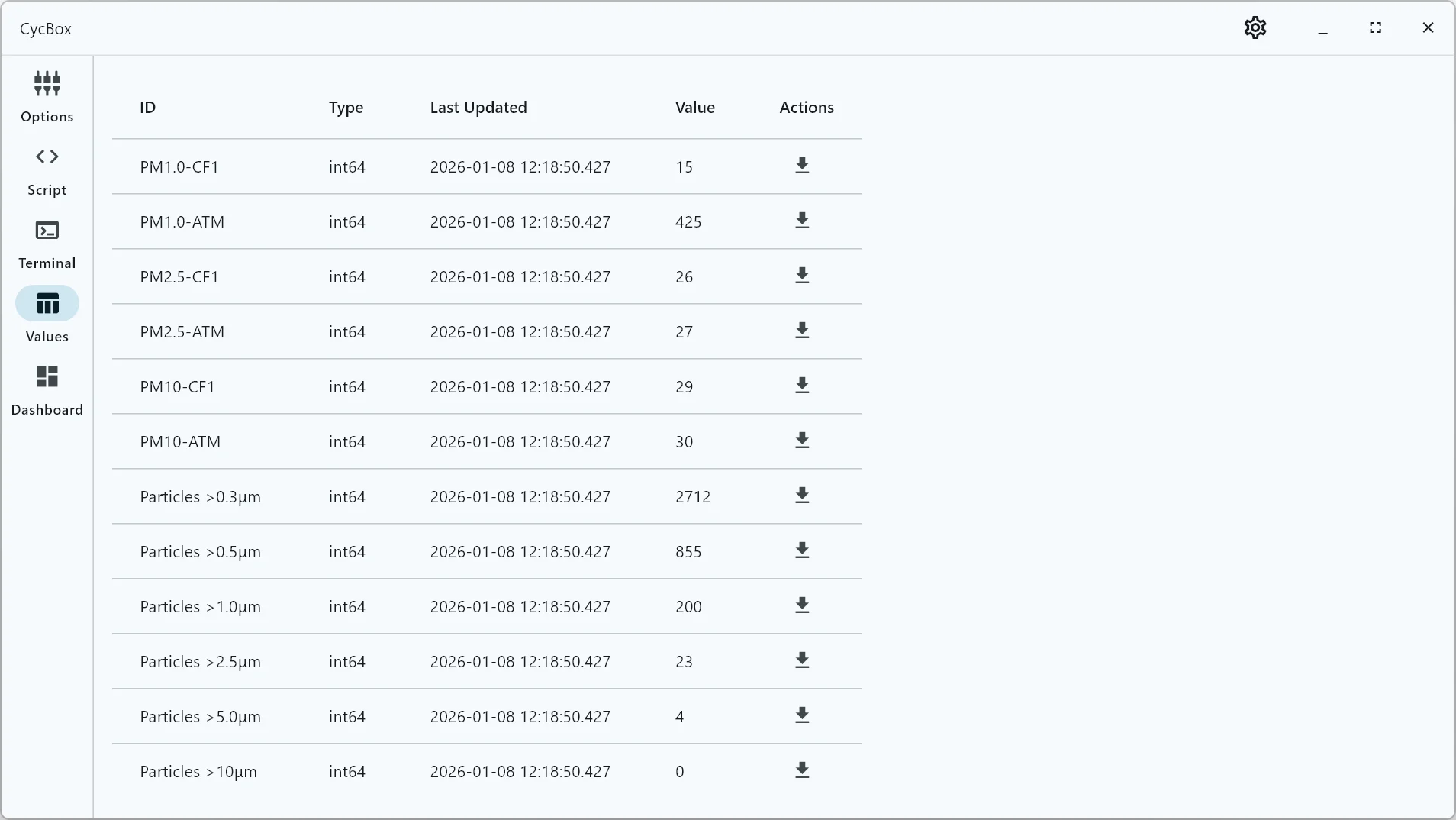
Real-Time Data Visualization
Display live data with customizable charts and plots. Features include screenshot capture for quick data reviews and seamless CSV export for further analysis.
More Features
- High-precision 1ms timer with low-latency response for guaranteed real-time performance.
- Multiple built-in checksum algorithms for automatic validation of outgoing and incoming data.
- Cross-platform support for Linux, Windows, and Android.
- Versatile debugging tools, including Serial-to-TCP, Serial-to-MQTT, and HTTP Reverse Proxy support.
Use Cases
IoT Device Development
Efficiently debug and test microcontroller projects like ESP32, STM32, and others. Seamlessly monitor AT commands, interpret sensor data, and validate protocol implementations in real-time for streamlined development processes.
Industrial Automation
Easily test and troubleshoot Modbus RTU/TCP devices, PLCs, and industrial sensors. Accurately verify command sequences and monitor fieldbus communication to ensure robust performance in automated systems.
Protocol Analysis
Effectively capture and analyze custom protocols with the power of built-in Lua scripting. Design custom data transformers to decode and extract valuable insights from binary streams, simplifying complex protocol analysis.
Automation Testing
Automate device testing with powerful scripting capabilities. Execute regression tests, validate hardware and software behavior, and ensure devices meet defined performance standards efficiently.